1. 医药器械检验检测
医药器械检验检测是指对医疗器械产品进行质量检验和性能验证的过程,旨在保障医疗器械产品的安全性、有效性和可靠性,确保其符合相关规范和标准的要求。在医药器械行业中,检验检测是非常重要的环节,涉及到产品的各个方面,包括材料、结构、性能、安全性等。医药器械检验检测研究的一个重要方向是质量控制和标准化。研究者可以通过建立有效的质量控制方法和流程,确保医疗器械产品在生产过程中的质量达到标准要求。同时,研究者还可以参与标准的修订和制定工作,促进医疗器械行业标准体系的完善和规范化。医药器械检验检测研究还可以聚焦于疾病预防和控制。通过对医疗器械产品的检验检测,可以及时发现可能存在的安全隐患,预防疾病传播和扩散。研究者可以探索医疗器械产品在疾病预防和控制中的作用,提出改进建议和措施。随着科学技术的不断进步,医药器械检验检测领域也在不断创新。研究者可以开展新技术和新方法的研究,如纳米技术、生物传感技术等,应用于医疗器械产品的检验检测中,提高检测的准确性、灵故、可靠性和效率。医药器械检验检测研究是一个涵盖多个方面的领域,需要跨学科合作,结合理论研究和实践经验,不断探索和创新,以提高医疗器械产品质量和安全性,保障人民的健康和生命安全相关123。
图 1. 医药器械检验检测
对于医院来讲,要想更好的拯救病患的生命,除了有优秀的职工队伍,高超的水平之外,还离不开一个重要的要素,即先进的设备。尤其是在科技高速发展的今天,医疗设备早就成为了医院发展过程中必不可少的重要要素。在实际的工作中,我们必须认真的开展设备的计量工作,只有这样才能够更好的了解设备的性能,更好的发挥出它们的意义和价值。假如在测量的时候出现了失误的话,就无法真正的反应状态,就会发生诊断不正确以及治疗不成功之类的问题。因此为了避免问题发生,我们必须要从主客观两个层次来分析设备合格率和检测率,这两个质量控制指标反映医疗设备的质量和一致性程度,因此需要结合医疗设备的具体情况,合理对医疗设备进行评价和监测,进而提高医疗仪器设备的管理质量,从而避免误诊误治现象的出现。具体来说,作为医疗单位,必须要提升工作者对检定活动的认知能力,确保他们都能够从真正意义上意识到检定活动存在的价值,强化计量工作的管控水平,认真分析具体状态,从最初的购置到后续的安装和使用等多个层次中,积极的开展好计量检测工作。除此之外,因为设备的品质和工作者的应用能力之间有很大的关系,所以我们必须要对工作者开展一系列的培训活动,增加他们的计量知识,帮助建立法制计量概念,强化医疗设备的计量检测管理意识,从思想认识上将医学计量验收并付诸行动,进而促进医学计量工作的发展。

图 2. 医药器械检验检测
相关论文:
1. Qing Ye, Chang-Yu Hsieh, Ziyi Yang, Yu Kang, Jiming Chen, Dongsheng Cao*, Shibo He*, Tingjun Hou*, A unified drug-target interaction prediction framework based on knowledge graph and recommendation system, Nature Communications, 2021, 12, 6775.
2. Jike Wang, Chang-Yu Hsieh, Mingyang Wang, Xiaorui Wang, Zhenxing Wu, Dejun Jiang, Benben Liao, Xujun Zhang, Bo Yang, Qiaojun He, Dongsheng Cao*, Xi Chen*, Tingjun Hou*, Multi-constraint molecular generation based on conditional transformer, knowledge distillation and reinforcement learning, Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3, 914-922.
3. Mingyang Wang, Zhe Wang, Huiyong Sun, Jike Wang, Chao Shen, Gaoqi Weng, Xin Chai, Honglin Li*, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, Deep learning approaches for de novo drug design: an overview, Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2022, 72, 135-144.
4. Dejun Jiang, Chang-Yu Hsieh, Zhenxing Wu, Yu Kang, Jike Wang, Ercheng Wang, Ben Liao, Chao Shen, Lei Xu, Jian Wu*, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, InteractionGraphNet: a novel and efficient deep graph representation learning framework for accurate protein-ligand interaction predictions, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 64, 18209-18232.
5. Chao Shen, Ye Hu, Zhe Wang, Xujun Zhang, Haiyang Zhong, Gaoang Wang, Xiaojun Yao, Lei Xu, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, Can machine learning consistently improve the scoring power of classical scoring functions? Insights into the role of machine learning in scoring functions, Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2021, 22, 497-514.
6. Chao Shen, Ye Hu, Zhe Wang, Xujun Zhang, Jinping Pang, Gaoang Wang, Haiyang Zhong, Lei Xu, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, Beware of the generic machine learning-based scoring functions in structure-based virtual screening, Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2021, 22, bbaa070.
7. Chao Shen, Junjie Ding, Zhe Wang, Dongsheng Cao, Xiaoqin Ding, Tingjun Hou*, From machine learning to deep learning: advances in scoring functions for computational docking, WIRES Computational Molecular Science, 2020, 10, e1429.
8. Xujun Zhang, Chao Shen, Xueying Guo, Zhe Wang, Gaoqi Weng, Qing Ye, Gaoang Wang, Qiaojun He, Bo Yang*, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, ASFP (Artificial Intelligence based Scoring Function Platform): a web server for the development of customized scoring functions, Journal of Cheminformatics, 2021, 13, 6.
9. Guoli Xiong, Yue Zhao, Lu Liu, Zhongye Ma, Aiping Lu, Yan Cheng, Tingjun Hou*, Dongsheng Cao*, Computational bioactivity fingerprint similarities to navigate the discovery of novel scaffolds, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 64, 7544-7554.
10. Xueping Hu, Liu Yang, Xin Chai, Yixuan Lei, Md Shah Alam, Lu Liu, Chao Shen, Dejun Jiang, Zhe Wang, Zhiyong Liu, Lei Xu, Kanglin Wan, Tianyu Zhang, Yuelan Yin, Dongsheng Cao*, Dan Li*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of novel DprE1 inhibitors via computational bioactivity fingerprints and structure-based virtual screening, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2022, in press.
11. Sheng Tian, Junmei Wang, Youyong Li, Dan Li, Lei Xu, Tingjun Hou*, The application of in silico drug-likeness predictions in pharmaceutical research, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2015, 86, 2-10.
12. 12. Tailong Lei, Huiyong Sun, Yu Kang, Feng Zhu. Hui Liu, Wenfang Zhou, Zhe Wang, Dan Li, Youyong Li, Tingjun Hou*, ADMET evaluation in drug discovery. 18. Reliable prediction of chemical-induced urinary tract toxicity by boosting machine learning approaches, Molecular Pharmaceutics,2017, 14, 3935-3953.
13. Tailong Lei, Fu Chen, Hui Liu, Huiyong Sun, Yu Kang, Dan Li, Youyong Li, Tingjun Hou*, ADMET evaluation in drug discovery. 17. Development of quantitative and qualitative prediction models for chemical-induced respiratory toxicity, Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2017, 14, 2407-2421.
14. Zhenxing Wu, Tailong Lei, Chao Shen, Zhe Wang, Dongsheng Cao, Tingjun Hou*, ADMET Evaluation in Drug Discovery. 19. Reliable Prediction of Human Cytochrome P450 Inhibition Using Artificial Intelligence Approaches, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2019, 59, 4587-4601.
15. 15. Ziyi Yang, Junhong He, Aiping Lu, Tingjun Hou*, Dongsheng Cao*, The Application of Negative Design to Design More Desirable Virtual Screening Library, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 63, 4411-4429.
16. Tailong Lei, Huiyong Sun, Yu Kang, Feng Zhu. Hui Liu, Wenfang Zhou, Zhe Wang, Dan Li, Youyong Li, Tingjun Hou*, ADMET evaluation in drug discovery. 18. Reliable prediction of chemical-induced urinary tract toxicity by boosting machine learning approaches, Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2017, 14, 3935-3953.
17. Zhenxing Wu, Dejun Jiang, Jike Wang, Chang-Yu Hsieh*, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, Mining Toxicity Information from Large Amounts of Toxicity Data, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 64, 6924-6936.
18. Xiaochen Zhang, Chengkun Wu, Zhijiang Yang, Zhenxing Wu, Jiacai Yi, Changyu Hsieh, Tingjun Hou*, Dongsheng Cao*, MG-BERT: leveraging unsupervised atomic representation learning for molecular property prediction, Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2021, 22, bbab152.
19. Zhenxing Wu, Dejun Jiang, Jike Wang, Xujun Zhang, Hongyan Du, Lurong Pan, Changyu Hsieh*, Dongsheng Cao*, Tingjun Hou*, Knowledge-based BERT: a method to extract molecular features like computational chemists, Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2022, bbac131.
20. Guoli Xiong, Zhenxing Wu, Jiacai Yi, Li Fu, Zhijiang Yang, Changyu Hsieh, Mingzhu Yin, Xiangxiang Zeng, Chengkun Wu, Aiping Lu, Xiang Chen, Tingjun Hou*, Dongsheng Cao*, ADMETlab 2.0: an integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties, Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(W1), W5-W14.
2. 代谢组学
代谢组学(metabonomics/metabolomics)是效仿基因组学和蛋白质组学的研究思想,对生物体内所有代谢物进行定量分析,并寻找代谢物与生理病理变化的相对关系的研究方式,是系统生物学的组成部分。其研究对象大都是相对分子质量1000以内的小分子物质。先进分析检测技术结合模式识别和专家系统等计算分析方法是代谢组学研究的基本方法。
代谢组学是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。之后得到迅速发展并渗透到多项领域,比如疾病诊断、医药研制开发、营养食品科学、毒理学、环境学,植物学等与人类健康护理密切相关的领域。基因组学和蛋白质组学分别从基因和蛋白质层面探寻生命的活动,而实际上细胞内许多生命活动是发生在代谢物层面的,如细胞信号释放(cell signaling),能量传递,细胞间通信等都是受代谢物调控的。代谢组学正是研究代谢组(metabolome)——在某一时刻细胞内所有代谢物的集合——的一门学科。基因与蛋白质的表达紧密相连,而代谢物则更多地反映了细胞所处的环境,这又与细胞的营养状态,药物和环境污染物的作用,以及其它外界因素的影响密切相关。因此有人认为,“基因组学和蛋白质组学告诉你什么可能会发生,而代谢组学则告诉你什么确实发生了。”(Bill Lasley, UC Davis)
代谢组学的概念来源于代谢组,代谢组是指某一生物或细胞在一特定生理时期内所有的低分子量代谢产物,代谢组学则是对某一生物或细胞在一特定生理时期内所有低分子量代谢产物同时进行定性和定量分析的一门新学科 (Goodacre,2004)。它是以组群指标分析为基础,以高通量检测和数据处理为手段,以信息建模与系统整合为目标的系统生物学的一个分支。
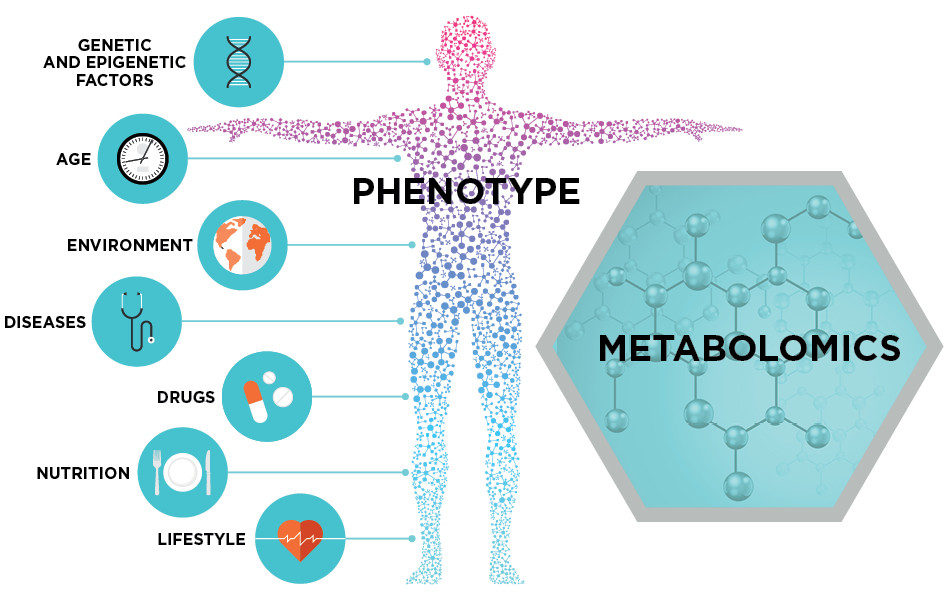
图 3. 代谢组学
相关文献:
1. Ercheng Wang, Huiyong Sun, Junmei Wang, Zhe Wang, Hui Liu, John Z.H. Zhang*, Tingjun Hou*, End-Point binding free energy calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: strategies and applications in drug design, Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119, 9478-9508.
2. Ercheng Wang, Gaoqi Weng, Huiyong Sun, Hongyan Du, Feng Zhu, Fu Chen, Zhe Wang, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 10. Impacts of Enhanced Sampling and Variable Dielectric Model on Protein-Protein Interactions, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019, 21, 18958-18969.
3. Gaoqi Weng, Ercheng Wang, Fu Chen, Huiyong Sun, Zhe Wang, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 9. Prediction reliability of binding affinities and binding poses for protein-peptide complexes, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019, 21, 10135-10145.
4. Fu Chen, Huiyong Sun, Junmei Wang, Feng Zhu, Hui Liu, Zhe Wang, Tailong Lei, Youyong Li, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 8. Predicting binding free energies and poses of protein-RNA complexes, RNA, 2018, 24, 1183-1194.
5. Huiyong Sun, Lili Duan, Fu Chen, Hui Liu, Zhe Wang, Peichen Pan, Feng Zhu, John Z. H. Zhang, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 7. Entropy effects on the performance of end-point binding free energy calculation approaches, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20, 14450-14460.
6. Fu Chen, Hui Liu, Huiyong Sun, Peichen Pan, Youyong Li, Dan Li, Tingjing Hou*, Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 6. Capability to predict protein-protein binding free energies and re-rank binding poses generated by protein-protein docking, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18, 22129-22139.
7. Huiyong Sun, Youyong Li, Mingyun Shen, Sheng Tian, Lei Xu, Peichen Pan, Yan Guan, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the Performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods. 5. Improved Docking Performance by Using High Solute Dielectric Constant MM/GBSA and MM/PBSA Rescoring, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16, 22035-22045.
8. Huiyong Sun, Youyong Li, Sheng Tian, Lei Xu, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the Performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods. 4. Accuracies of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methodologies Evaluated by Various Simulation Protocols using PDBbind Data Set, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16, 16719-16729.
9. Lei Xu, Huiyong Sun, Youyong Li, Junmei Wang, Tingjun Hou*, Assessing the Performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods. 3. The Impact of Force Fields and Ligand Charge Models, Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2013, 117, 8408-8421.
10. Tingjun Hou*, Junmei Wang, Youyong Li, Wei Wang*, Assessing the performance of the Molecular Mechanics/Poisson Boltzmann Surface Area and Molecular Mechanics/ Generalized Born Surface Area methods. II. The accuracy of ranking poses generated from docking, Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2011, 32, 866-877.
11. Tingjun Hou*, Junmei Wang, Youyong Li, Wei Wang*, Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods: I. The accuracy of binding free energy calculations based on molecular dynamics simulations, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2011, 51, 69-82.
12. Ercheng Wang, Weitao Fu, Dejun Jiang, Huiyong Sun, Junmei Wang, Xujun Zhang, Gaoqi Weng, Hui Liu, Peng Tao, and Tingjun Hou*, VAD-MM/GBSA: A Variable Atomic Dielectric MM/GBSA Model for Improved Accuracy in Protein–Ligand Binding Free Energy Calculations, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2021, 61, 2844-2856.
13. Ercheng Wang, Hui Liu, Junmei Wang, Gaoqi Weng, Huiyong Sun, Zhe Wang, Yu Kang, Tingjun Hou*, Development and Evaluation of MM/GBSA Based on a Variable Dielectric GB Model for Predicting Protein-Ligand Binding Affinities, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2020, 60, 5353-5365.
14. Gaoqi Weng, Ercheng Wang, Zhe Wang, Hui Liu, Feng Zhu, Dan Li, Tingjun Hou*, HawkDock: a web server to predict and analyze the protein-protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA, Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47, W322-W330.
15. Hui Liu, Tingjun Hou*, CaFE: a tool for binding affinity prediction using end-point free energy methods, Bioinformatics, 2016, 32, 2216-2218.
16. Zhe Wang, Xuwen Wang, Youyong Li, Tailong Lei, Ercheng Wang, Dan Li, Yu Kang, Feng Zhu, Tingjun Hou*, farPPI: a webserver for accurate prediction of protein-ligand binding structures for small-molecule PPI inhibitors by MM/PB(GB)SA methods, Bioinformatics, 2019, 35, 1777-1779.
17. Tingjun Hou*, Nan Li, Youyong Li, Wei Wang*, Characterization of domain-peptide interaction interface: prediction of SH3 domain-mediated protein-protein interaction network in yeast by generic structure-based models, Journal of Proteome Research, 2012, 11, 2982-2995.
18. Zheng Xu#, Tingjun Hou# (co-first author), Nan Li, Yang Xu, Wei Wang, Proteome-wide detection of Abl1 SH3 binding peptides by integrating computational prediction and peptide microarray, Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2012, 11, O111.010389.
19. Sheng Tian, Huiyong Sun, Youyong Li, Dan Li, Tingjun Hou*, Development and evaluation of an integrated virtual screening strategy by combining molecular docking and pharmacophore searching based on multiple protein structures, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2013, 53, 2743-2756.
20. Xiaotian Kong, Huiyong Sun, Peichen Pan, Feng Zhu, Shan Chang, Lei Xu, Youyong Li, Tingjun Hou*, Importance of protein flexibility in molecular recognition: a case study on Type-I1/2 inhibitors of ALK, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20, 4851-4863.
3. 中药现代化和可解释性研究
中药现代化和可解释性研究是一个重要的领域,旨在将传统中药的疗效与现代科学技术相结合,实现中药疗效的科学验证和可靠性评估。在传统中药中,虽然有很多药物具有显著的疗效,但其药理机制和作用目标往往是复杂而模糊的。这导致了中药在科学研究和临床应用中缺乏可解释性,难以被现代医学所接受和理解。因此,中药现代化和可解释性研究的重要性凸显出来。在中药现代化方面,研究人员可以通过现代科学技术的手段,如高通量筛选、基因组学、蛋白质组学等,解析中药的活性成分、药理作用机制和药效评估。通过这些方法,可以更好地理解中药的药理学特性和作用机制,为中药的现代化应用提供科学依据。同时,中药的可解释性研究也至关重要。通过结合人工智能、机器学习等技术,可以构建中药药理模型,预测中药复方的药效和药物相互作用,提高中药的治疗效果和安全性。此外,采用系统生物学方法对中药-靶标网络进行分析,可以揭示中药在细胞和分子水平上的作用机制,增强中药的可解释性和临床应用的科学性。总的来说,中药现代化和可解释性研究的发展对于传统中药的现代应用意义重大。通过结合现代科学技术和传统药物学知识,可以实现中药疗效的科学解释、评估和优化,推动中医药在现代医学领域的发展和应用。
相关文献:
1. Rui Shi, Peichen Pan, Rui Lv, Chongqing Ma, Enhui Wu, Ruochen Guo, Zhihao Zhao, Hexing Song, Joe Zhou, Yang Liu, Guoqiang Xu, Tingjun Hou*, Zhenhui Kang*, Jian Liu*, High-throughput glycolytic inhibitor discovery targeting glioblastoma by graphite dots-assisted LDI mass spectrometry, Science Advances, 2022, 8, eabl4923.
2. Xin Chai, Huiyong Sun, Wenfang Zhou, Changwei Chen, Luhu Shan, Yuhui Yang, Junzhao He, Jinping Pang, Liu Yang, Xinyue Wang, Sunliang Cui, Yaqin Fu, Xiaohong Xu, Lei Xu, Xiaojun Yao, Dan Li*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of N-(4-(Benzyloxy)-phenyl)-sulfonamide Derivatives as novel antagonists of the human androgen receptor targeting the activation function 2, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2022, 65, 2507-2521.
3. Jinping Pang, Chao Shen, Wenfang Zhou, Yunxia Wang, Luhu Shan, Xin Chai, Ying Shao, Xueping Hu, Feng Zhu, Danyan Zhu, Li Xiao, Lei Xu, Xiaohong Xu, Dan Li*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of novel antagonists targeting the DNA binding domain of androgen receptor by integrated docking-based virtual screening and bioassays, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2022, 43, 229-239.
4. Weitao Fu, Minkui Zhang, Jianing Liao, Qing Tang, Yixuan Lei, Zhou Gong, Luhu Shan, Mojie Duan, Xin Chai, Jinping Pang, Chun Tang, Xuwen Wang, Xiaohong Xu, Dan Li*, Rong Sheng*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of a novel androgen receptor antagonist manifesting evidence to disrupt the dimerization of the ligand-binding domain via attenuating the hydrogen-bonding network, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 64, 17221-17238.
5. Qin Tang, Weitao Fu, Minkui Zhang, Ercheng Wang, Lvhu Shan, Xin Chai, Jinping Pang, Xuwen Wang, Xiaohong Xu, Lei Xu, Dan Li*, Rong Sheng*, Tingjun Hou*, Novel androgen receptor antagonist identified by structure-based virtual screening, structural optimization, and biological evaluation, European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2020, 192, 112156.
6. Wenfang Zhou, Mojie Duan, Weitao Fu, Jinping Pang, Qin Tang, Huiyong Sun, Lei Xu, Shan Chang, Dan Li*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of Novel Androgen Receptor Ligands by Structure-based Virtual Screening and Bioassays, Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2019, 16, 416-427.
7. Xueping Hu, Jinping Pang, Jintu Zhang, Chao Shen, Xin Chai, Ercheng Wang, Haiyi Chen, Xuwen Wang, Mojie Duan, Weitao Fu, Lei Xu, Yu Kang, Dan Li*, Hongguang Xia*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of novel GR ligands towards druggable GR antagonist conformations identified by MD Simulations and Markov state model analysis, Advanced Science, 2022, 9, 2102435.
8. Weitao Fu, Ercheng Wang, Di Ke, Hao Yang, Lingfeng Chen, Jingjing Shao, Xueping Hu, Lei Xu, Na Liu*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of a novel Fusarium Graminearum Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase (FgGpmk1) inhibitor for the treatment of fusarium head blight, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 64, 13841-13852.
9. Yuan Wang, ZheWang, Jiacheng Liu, Yunwen Wang, Rui Wu, Rong Sheng*, Tingjun Hou*, Discovery of novel HBV capsid assembly modulators by structure-based virtual screening and bioassays, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 36, 116096.
4. 基于多尺度分子模拟的靶标-配体识别作用机制研究
传统实验方法(X-ray和NMR)可以有效地表征蛋白或蛋白-配体的静态或准静态结构,但是无法描述配体−靶标之间的动态识别过程。在这种情况下,全原子模拟(包括常规动力学模拟和增强采样动力学模拟)可以辅助实验技术捕捉原子层次的动力学和热力学作用机制。我们采用常规动力学模拟和增强采样动力学模拟技术(如元动力学、伞形采样、适配性偏向力等方法)揭示了许多复杂的分子机制,开展了药物分子耐药性机制、ABC转运蛋白作用机制、小分子保留时间计算等方面的理论分析 [1-15]。例如,通过元动力学模拟对小分子抑制剂结合与解离过程中势能面的表征,我们发现ROS1激酶中G2032R突变可以从两方面影响crizotinib的结合,其中ROS1中僵硬的P-loop区既可以直接降低crizotinib的结合,同时又可以显著缩减crizotinib在G2032R突变型ROS1中的保留时间,从而产生强烈耐药性 [11](图5)。

图 5. Crizotinib 从 G2032R-ROS1 解离的能景图
相关文献:
1. Haiyi Chen, Rui Zhou, Jinping Pang, Yue Guo, Jiawen Chen, Yu Kang*, Mojie Duan*, Tingjun Hou*, Molecular view on the dissociation pathways and transactivation regulation mechanism of nonsteroidal GR ligands, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2022, in press.
2. Haiyi Chen, Yu Kang, Mojie Duan*, Tingjun Hou*, Regulation mechanism for the binding between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and host angiotensin-converting enzyme II, The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12, 6252-6261.
3. Yongchang Xu, Haiyi Chen, Huimin Zhang, Saif Ullah, Tingjun Hou*, Youjun Feng*, The MCR-3 inside linker appears as a facilitator of colistin resistance, Cell Reports, 2021, 35, 109135.
4. Ye Jin, Mojie Duan, Xuwen Wang, Xiaotian Kong, Wenfang Zhou, Huiyong Sun, Hui Liu, Dan Li, Huidong Yu, Youyong Li*, Tingjun Hou*, Communication between the ligand-binding pocket (LBP) and the activation function-2 (AF2) domain of androgen receptor revealed by molecular dynamics simulations, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2019, 59, 842-857.
5. Na Liu, Wenfang Zhou, Yue Guo, Junmei Wang, Weitao Fu, Huiyong Sun, Dan Li, Mojie Duan*, Tingjun Hou*, Molecular Dynamics Simulations Revealed the Regulation of Ligands to the Interactions between Androgen Receptor and Its Coactivator, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2018, 58, 1652-1661.
6. Huiyong Sun, Youyong Li, Mingyun Shen, Dan Li, Yu Kang. Tingjun Hou*, Characterizing drug-target residence time with metadynamics: how to achieve dissociation rate efficiently without losing accuracy against much time-consuming approaches, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2017, 57, 1895-1906.
7. Mojie Duan, Na Liu, Wenfang Zhou, Dan Li, Minghui Yang*, Tingjun Hou*, Structural diversity of ligand-binding androgen receptors revealed by microsecond long molecular dynamics simulations and enhanced sampling, Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2016, 12, 4611-4619.